- Update 語法中有 where 的搜尋條件,因此會使用到相關索引的 "seek" 或 "scan",找出相關資料在進行更新。所以如同 "Select" 查詢一樣,"where" 條件將會決定某些 "index" 是否能快速找尋相關資料為重要因素
- CASE 1
update tbPerson01 set FirstName = 'Stone' where BusinessEntityID in (300)
update tbPerson02 set FirstName = 'Stone' where BusinessEntityID in (300)
update tbPerson01 set FirstName = 'Stone' where LastName in ('Chen')
update tbPerson02 set FirstName = 'Stone' where LastName in ('Chen')
- Result:
- "Update" 的 "Where" 條件可以所用到 "index" 的 "鍵值資料行",在尋找資料上會較為快速
- "scan" (掃描) 與 "seek" (搜尋) 在查詢效率上的差異
- CASE 2
- index 造成額外索引維護成本
- 資料行如果剛好在 "index" 的 "鍵值資料行"或是 "include"內的資料行,此 "update"操作需將相關 "index" 一起維護,會增加額外成本
- 資料庫使用 Adventure Works for SQL Server 2012 的資料表 Person.Person 創建 2 個 table 如下
- tbPerson01
- unique Clustered index (BusinessEntityID)
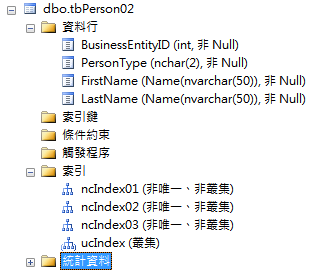
- tbPerson02:
- unique Clustered index (BusinessEntityID)
- NonClustered index (PersonType)
- NonClustered index (FirstName)
- NonClustered index (LastName)
update tbPerson01 set FirstName = 'Stone' where BusinessEntityID in (300)
update tbPerson02 set FirstName = 'Stone' where BusinessEntityID in (300)
- Result:
- "update" 操作只會真對受到影響的 "index" 進行維護,包括其它 "index" 的 "鍵值資料行" 以及 "index" 所內含的 "include" 資料行
- "update" 操作所設定 "where" 條件如同 "select" 一樣,會選擇適當的 "index"來進行資料過濾
- REF:













沒有留言:
張貼留言